Connecting an adviser with your children
How parents and advisers can work together to manage intergenerational wealth transfers.

.
We’re told our time horizon shrinks as we age. This makes sense, because the closer we get to retirement, the less time we have left to accumulate wealth. And the nearer we come to having to eventually draw down on that wealth.
But retirement often throws up a whole new set of priorities. Instead of our own time horizon, we’re now thinking about our children’s time horizon; and, as they may have their own families, even their children’s time horizon.
Suddenly, the priority is not just to make your wealth last, but to preserve it for the next generation. And that’s where the real power of advice lies: its ability to transform families by building intergenerational wealth.
The intergenerational wealth opportunity
Australia is nearing the crest of a retirement wave. As the baby boomer generation looks to pass on wealth, those in receipt of it will likely need guidance.
For the emerging generation of wealth builders, what were once reasonably straightforward considerations around saving and budgeting may suddenly become more substantial.
Figure 1: We have gone from an accumulation system to decumulation
Australians moving into retirement by year
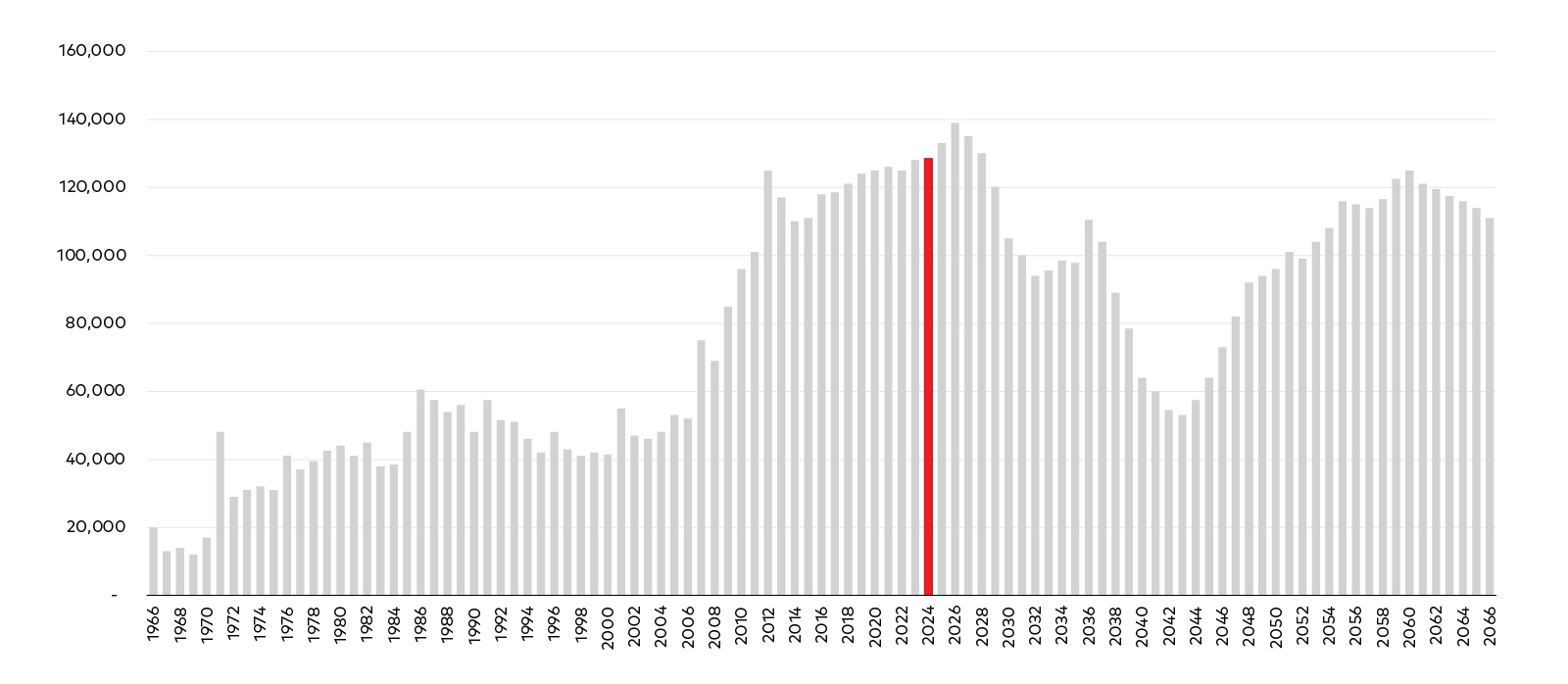
Source: August 2021 Census—Australians turning 55 by year, Australian Bureau of Statistics.
And for both the younger and older generations, conversations around estate planning, inheritance, business succession, the family home, tax issues, and aged care can open an emotional can of worms.
Building trust with both cohorts is essential before these conversations can take place. Putting the time in now is worth it given the potential size of the opportunity.
Estimating wealth in aggregate is notoriously difficult, especially when you factor in businesses, home contents, non-superannuation investments and non-financial assets. But with some modelling, we can get a reasonable idea of the wealth set to change hands.
According to CoreData Research, the baby boomer generation holds around $4.9 trillion in total assets. This wealth is held by over 4 million baby boomers, including a small group of wealthy “baby boomers” with $1.3 trillion in assets.
Figure 2: The size of the opportunity: 2% of baby boomers are high net worth baby boomers, while 1% of total population are high net worth investors.
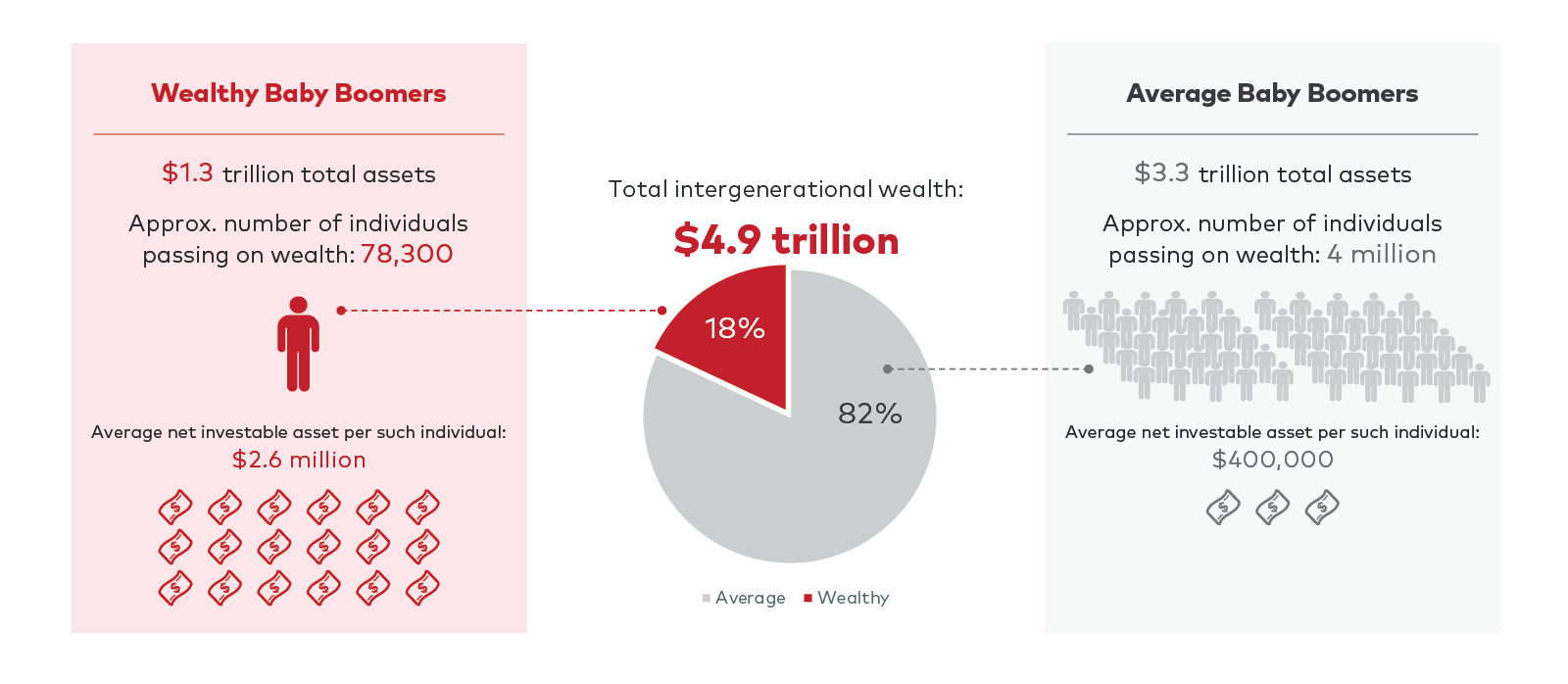
Source: CoreData modelling (updated November 2023).
How this wealth gets passed on could be the biggest financial change in Australia’s history. It could also be the biggest opportunity in advice that has ever existed.
Building trust across generations
We know it’s critical for advisers to reach Australians at a younger stage of life. But there’s a lot of groundwork that needs to be done before an adviser can start advising your children.
Talking to other people’s children about money is a delicate matter. Wealth transfers and inheritance planning are not regular topics of conversation at the family level. Understandably, many families find subjects such as death and the future division of wealth as unpleasant and potentially sensitive, especially when multiple heirs are involved.
Building trust across generations helps facilitate open discussions about the intended treatment of assets, as well as the ‘who’, ‘how’ and ‘when’ of transferring wealth. This requires talking to both generations, not just the older one.
So, how should advisers ideally approach intergenerational wealth transfers with you and your children?
Advisers may have a strong, long-standing relationship with you, but that doesn’t mean they can automatically win trust from your children.
Here are some important considerations for advisers when engaging clients across the generational divide:
- Younger clients describe themselves through their investments: Younger generations want to invest in things they feel good about. They’re looking for advice to ensure their investments align with their values.
- Building a client value proposition: The value advisers provide to you doesn’t necessarily matter to your children. Advisers need to demonstrate the value and utility of their advice to your children.
- Focus on the tech stack: Millennials and zoomers are technology-first generations. Advisers should meet them where they are when it comes to harnessing technology in their interactions and advice delivery.
Technology is no substitute for real human connection, but in the right context it can help advisers engage on a deeper level, communicate the full value of their advice, and make certain tasks quicker and easier.
When it comes to ensuring investments are sufficiently diversified, staying informed about the markets, modelling different scenarios, and monitoring investments, a significant proportion of clients prefer technology to be involved.
For trust and confidence, feeling listened to, and knowing their goals are understood, clients overwhelmingly prefer human delivery.
Figure 3: Investors prefer emotional and financial planning services to be delivered by humans
Investor stated preferences (top 10 preferred for human delivery)
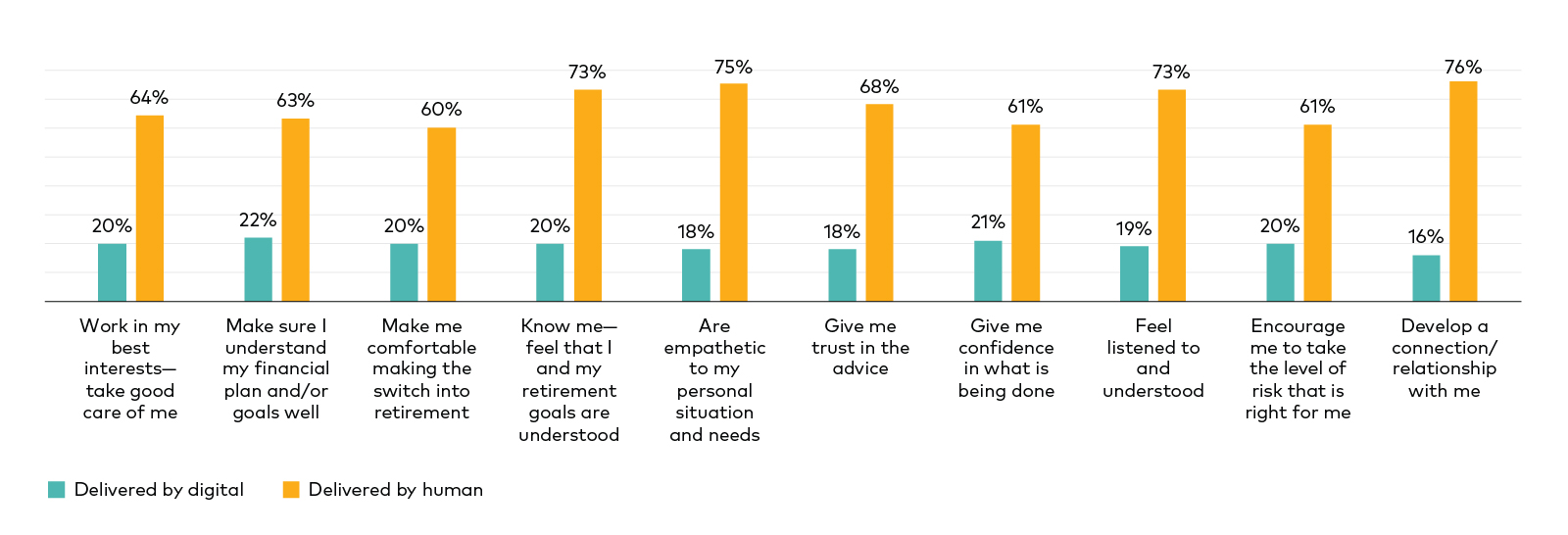
Figure 4: Investors have highest preference for digital services for portfolio outcomes and functional tasks
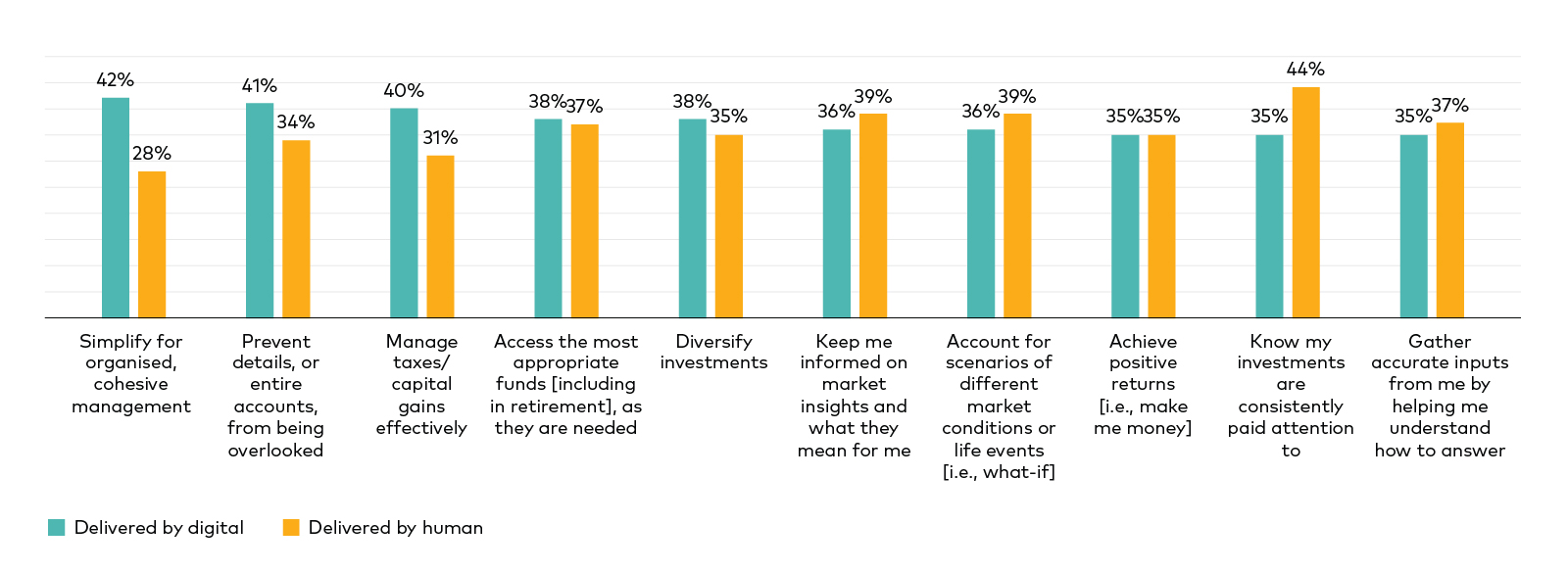
Notes: Quantitative research conducted by Vanguard in July 2021. In this figure, all 1,518 clients answered the question. They were presented with the micro-interactions and asked to rate whether they preferred that service to be delivered by a human or a digital adviser. The ratings were presented on an 11-point scale, where 0 meant “Completely delivered by a human” and 10 meant “Completely delivered by a digital service.” Clients were considered to prefer human delivery if their rating was between 0 and 4 and digital delivery of the service if their rating was between 6 and 10. Sources: Vanguard and Escalent, 2021.
Vanguard
April 24
vanguard.com.au





